Skip Ahead:
- The ever-present threat
- How hackers gain access
- What’s at risk?
- How to protect against attacks
- Start securing your own systems
The ever-present threat
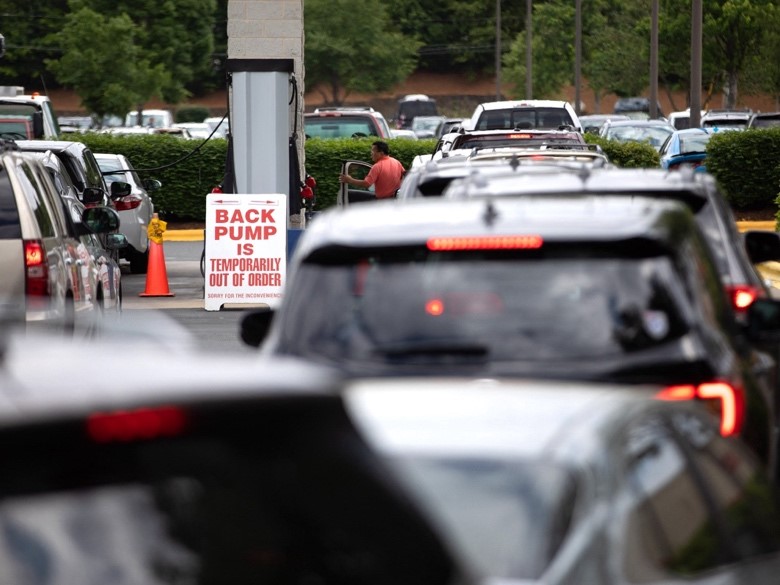

In May 2021, one of the largest fuel pipelines in the United States came to a grinding halt, and all it took was one compromised password. Hackers exploited an outdated VPN without multi-factor authentication to infiltrate Colonial Pipeline’s systems. Within hours, federal agents arrived at the company’s Georgia headquarters as monitors blinked with ransomware demands: $4.4 million in Bitcoin to restore access.
Critical systems were frozen, forcing the company to shut down 5,500 miles of pipeline—cutting off nearly half of the East Coast’s fuel supply. Panic-buying drained gas stations, and federal agencies scrambled to respond. The attack wasn’t just a company’s crisis—it was a national emergency.
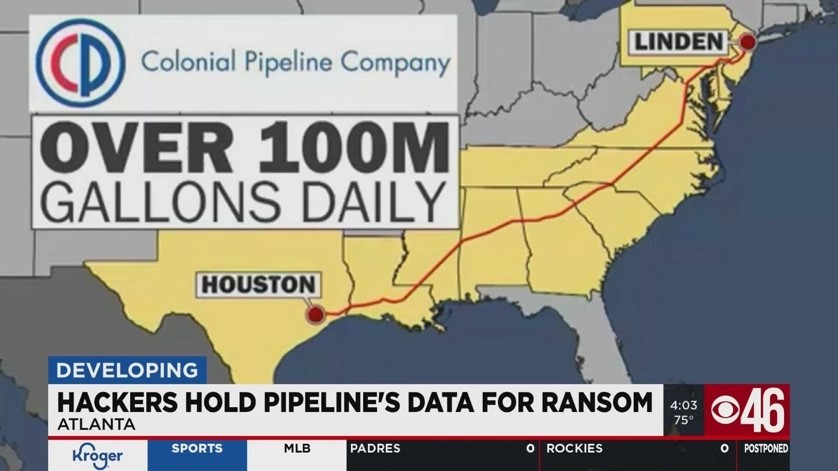
As manufacturing lines, equipment, and communication systems grow increasingly sophisticated, their vulnerability to cyber-attacks escalates. Any device with an IP address can serve as an entry point for hackers and malicious actors, potentially crippling a company’s network and local area network (LAN).
Pharmaceutical and drug manufacturing firms are particularly at risk. These companies are lucrative targets for cybercriminals and are relatively unprotected. Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) and pharmaceutical manufacturers are integrating more technology into their operations, and devices programmed to transmit data via wireless connections (e.g. Bluetooth) or the internet can be compromised. Once these devices are breached, hackers can infiltrate a company’s network, accessing sensitive software, data, and communications to cause significant disruption.
How hackers gain access
Any device or piece of equipment that communicates through wireless connection or Wi-Fi is vulnerable to security breaches. For some wireless connections, such as Bluetooth, a hacker needs to be within range to exploit these vulnerabilities. However, hackers have been known to access devices and networks by simply positioning themselves close enough to a building to establish a remote connection. If a device is connected to the internet, it opens the possibility for hackers to infiltrate from virtually anywhere from across the globe.
What’s at risk?
Hackers generally focus on two main targets within the pharmaceutical industry: administrative data and manufacturing equipment. Administrative data encompasses email communications, accounting records, and other critical documents. Manufacturing equipment ranges from laboratory instruments to production lines and utility controls.
Once a hacker breaches the system, they can halt production lines, disrupt email communications, or block access to essential documents and financial data, often demanding a ransom to restore access. If the ransom goes unpaid, they might even threaten to delete vital information, such as completed batch records for manufactured products.
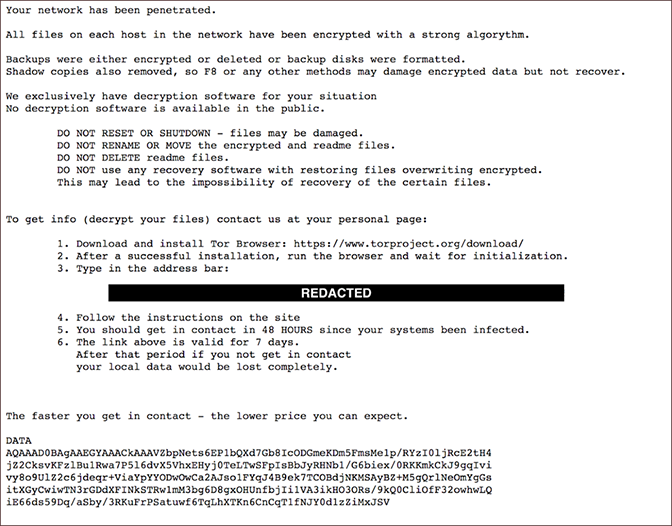
Moreover, hackers can manipulate data or alter formulations discreetly, potentially resetting configurations to hazardous levels. The repercussions of such tampering might not become apparent immediately, but they can lead to severe consequences down the line.
The threat posed by these cyberattacks is profound. Not only can they devastate a company almost instantly, but there’s also a broader danger: patients depending on these medications could face critical shortages, putting lives at risk.
How to protect against attacks
So, what stops a hacker? There are several tools at our disposal.
Firewalls
Firewalls are crucial for network security within any company, acting as gatekeepers that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. For example, a basic firewall may block IPs from specific countries. By scrutinizing each network packet, firewalls ensure that only safe and legitimate traffic is permitted, safeguarding the network’s integrity. It’s good practice to create the firewall at the time you build the network to protect that communication.
Two-factor Authentication

Implementing measures like two-factor authentication and enforcing strong password policies can significantly lower the risk of cybersecurity breaches. While stealing a simple password may be relatively easy, the additional verification step in two-factor authentication poses a much tougher challenge for hackers to bypass. At the time of their cyberattack, Colonial Pipeline did not have two-factor authentication in place. Implementing this security measure could have likely prevented the disaster they encountered.
Adopting Simpler Technology
Adopting simpler technology for certain protocols and processes can help reduce risks. For example, you can’t hack into a basic, non-programmable thermostat to change the temperature settings in someone’s home. However, with a smart thermostat that connects to the internet, it’s possible. We often trade security for convenience without realizing it. Especially for important equipment, it’s crucial to use designs and materials that are harder to hack. For instance, using a system like Modbus to communicate with devices allows you to monitor equipment safely without the risk of remote tampering.
Maintain Regular Backups
Maintain regular backups for everything in your facility, from manufacturing to accounting records. The frequency of backups should depend on the data’s volatility. For example, static data like equipment recipes might only need daily backups with weekly deletion of old data. For constantly changing data, like accounting records, consider minute-by-minute backups to prevent data loss from cyberattacks. For example, PharmaPhixx engineers implemented two-minute interval backups for a company. Several years later, they were hacked, but they could ignore the ransom demand because they had access to all their data in these backups.
Backups are crucial for other risks too, not just cybersecurity threats. One project we worked on involved a company losing PLC data during a power outage caused by a storm because the backup battery had failed, highlighting the importance of regular system checks and backup maintenance.
Stay Up-To-Date
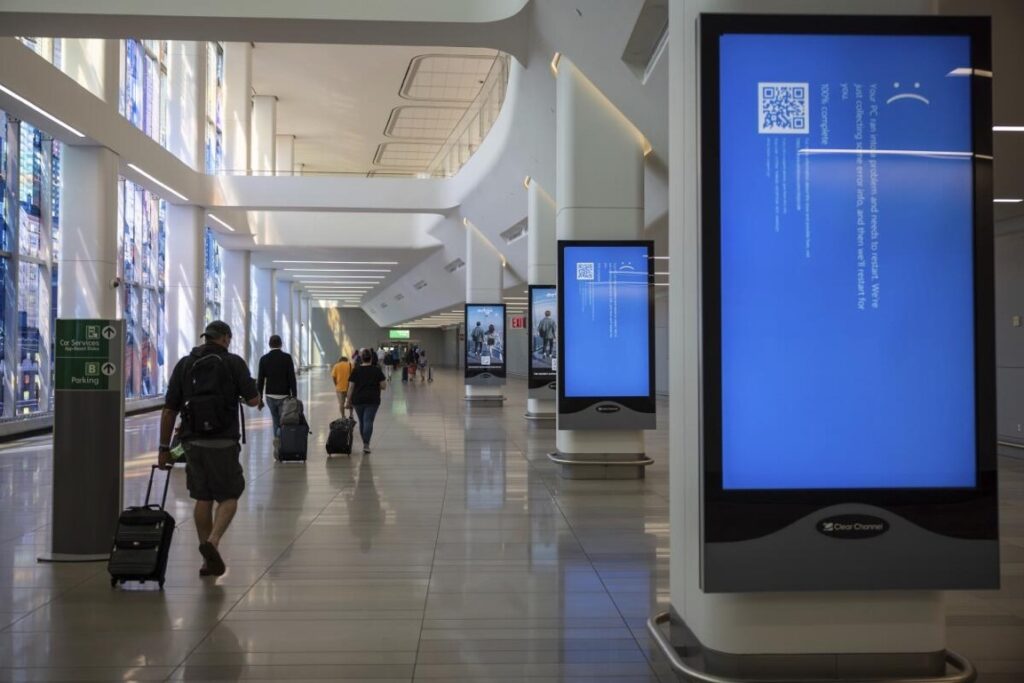

Once you set up your firewalls, backups, and processes, to maintain protection, it’s crucial to keep your software up to date. Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats. When new viruses or hacking techniques emerge, update your firewall to defend against these new threats. Additionally, always test updates before deploying them to prevent disruptions, such as the CrowdStrike update that caused widespread outages for major airlines (NBC News, 2022).
Keep a Lifeguard on Duty
Have an IT department or hire a third-party service to ensure your network is secure. They should use monitoring software that acts as a safeguard against unauthorized attempts to access your system. For example, if a bot repeatedly tries to enter through a remote access port, the firewall can detect and block it, especially if the IP address originates from an unrecognized or suspicious source. This proactive defense helps prevent unauthorized access and secures your network against potential threats.
Start securing your own systems
As facilities increasingly rely on sophisticated, internet-connected equipment, the potential for disruptive cyber threats grows. To defend against these threats, companies should employ multiple layers of security measures.
These include:
- Firewalls: Act as gatekeepers to monitor and control network traffic.
- Two-factor Authentication: Adds a layer of security, making it harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Simpler Technology: Uses less hackable technology for critical controls.
- Regular Backups: Ensures data recovery in the event of a cyberattack.
- Software Updates: Keeps security software up to date to defend against new threats.
- Proactive Monitoring: Maintains continuous oversight to prevent unauthorized access.
Implementing these strategies is quicker and simpler than you might think. In just a few weeks, you can audit, plan, and deploy measures that safeguard your business against severe security breaches that have the potential to disrupt operations, erase critical data, or cause drug shortages that harm patients.
PharmaPhixx offers robust cybersecurity solutions designed to safeguard your networks, administrative data, and manufacturing equipment. We start with a comprehensive audit to pinpoint vulnerabilities and define the scope of necessary security enhancements, ensuring that every potential risk to your system is identified and addressed. Following the audit, we quickly implement customized security measures tailored to your specific needs. These measures include the installation of advanced firewalls to block unauthorized access, the setup of automatic backups to ensure data integrity, and continuous monitoring systems to detect and respond to threats in real time.
If you are looking to secure your systems against cyber threats, reach out to PharmaPhixx today!
Works Cited
- America’s Cyber Defense Agency. (n.d.). 4 Things You Can Do to Keep Yourself Cyber Safe [Webpage]. CISA. https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/news/4-things-you-can-do-keep-yourself-cyber-safe
- Atlanta News First. (2021, May 10). Coverage of the Colonial Pipeline Cyber Attack [YouTube video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e2S4kpVPB3E
- Bertrand, N. (2021, June 8). Colonial Pipeline CEO tells Senate cyber defenses were compromised ahead of hack. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/business/colonial-pipeline-ceo-tells-senate-cyber-defenses-were-compromised-ahead-hack-2021-06-08/
- Cisco. (n.d.). What is a Firewall? [Webpage]. Cisco Systems. https://www.cisco.com/site/us/en/learn/topics/security/what-is-a-firewall.html
- CrowdStrike. (n.d.). Ransomware Examples [Webpage]. CrowdStrike. https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/cybersecurity-101/ransomware/ransomware-examples/
- Cyrus, L. (Photographer). (2021). Cars wait in line at a gas station where a sign is posted “Back pump is temporarily out of order” [Photograph]. AFP/Getty Images. https://www.gettyimages.com/photos/logan-cyrus
- Iwamura, Y. (Photographer). (2021). Displays show a blue error message at LaGuardia Airport in New York after a faulty software update [Photograph]. Associated Press. https://www.ap.org
- NBC News. (2022, May 14). Mass cyber outage at airports, businesses, broadcasters: CrowdStrike. https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/mass-cyber-outage-airports-businesses-broadcasters-crowdstrike-rcna162664


